Cuando creamos un programa que realiza actualizaciones de la base de datos como por ejemplo una carga masiva, es interesante poder ver los mensajes y el estado de cada una de las actualizaciones en un Log que podremos consultar cuando sea necesario desde las transacciones que nos proporciona SAP.
Estas son:
- SLG0 : Crear objeto y subobjeto del Log.
- SLG1: Visualizar Logs.
- SLG2: Borrar Logs.
ESTRUCTURA DEL LOG:
Antes de nada, veamos la información que nos proporciona un Log: Contiene información de cabecera ( tipo , creador, nº de log, Fecha, Programa desde el que se ha creado el log…) y un listado de mensajes que pueden ser de 3 tipos: error, warning y correcto.
En el listado de mensajes podremos filtrar por tipo de mensaje simplemente pulsando en la barra el tipo que queramos ver.
CREAR UN LOG
1. SLG0-El primer paso es crear el objeto y sub-objeto log
Es una forma de clasificar los logs , deberemos dar un nombre al objeto y subobjeto con el que luego crearemos nuestro log.
2. Modulos de funciones Application Log
Podemos usar varias funciones para crear el log, todas ellas empiezan por BAL_LOG*, las más importantes y en el orden que debemos utilizarlas son:
| DATA: ls_log_header TYPE bal_s_log, gv_log_handle TYPE balloghndl. CALL FUNCTION ‘BAL_LOG_CREATE’ EXPORTING i_s_log = ls_log_header IMPORTING e_log_handle = gv_log_handle EXCEPTIONS log_header_inconsistent = 1 OTHERS = 2. IF sy-subrc <> 0. ENDIF. |
- Iniciar el Log -> BAL_LOG_CREATE
En primer lugar, debemos abrir el log con este módulo de funciones, pasándole la estructura de la cabecera del log (ls_log_header) que contendrá entre otras cosas el nombre del objeto y subobjeto que hemos creado previamente.
- Añadir mensajes al Log:
BAL_LOG_MSG_ADD , BAL_LOG_MSG_ADD_FREE_TEXT , BAL_LOG_MSG_CUMULATE
| CALL FUNCTION ‘BAL_LOG_MSG_ADD_FREE_TEXT’ EXPORTING i_log_handle = gv_log_handle i_msgty = lv_tipo *Puede ser ‘E’,’W’,’A’,’S’ i_probclass = lv_probclass i_text = lv_texto EXCEPTIONS log_not_found = 1 msg_inconsistent = 2 log_is_full = 3 OTHERS = 4. IF sy-subrc <> 0. ENDIF. |
Ejemplo: Con texto libre: En lv_texto podemos añadir el texto que nosotros queramos:
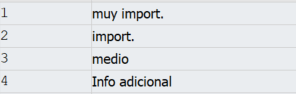
Lv_probclass puede tomar 4 valores:
Si queremos por ejemplo mostrar los mensajes que nos ha devuelto una llamada CALL TRANSACTION (l_s_msg) podremos utilizar:
| CALL FUNCTION ‘BAL_LOG_MSG_ADD’ EXPORTING i_log_handle = gv_log_handle i_s_msg = l_s_msg EXCEPTIONS log_not_found = 1 msg_inconsistent = 2 log_is_full = 3 OTHERS = 4 |
- Grabar el Log:
Para poder consultar el log que hemos creado desde la transacción SLG1 tenemos que guardarlo. Si no lo hacemos el log solamente estará disponible durante la ejecución del programa, puede ser útil si solo queremos ver el resultado cuando termine de ejecutarse el programa y si este se ejecuta en modo online. Al guardar el log, se le asigna un número, durante la ejecución del programa este número es temporal.
| CALL FUNCTION ‘BAL_DB_SAVE’ EXPORTING i_save_all = ‘X’ EXCEPTIONS log_not_found = 1 save_not_allowed = 2 numbering_error = 3 OTHERS = 4. |
- Mostrar el resultado del Log:
| call function ‘BAL_DSP_LOG_DISPLAY’ exceptions others = 1. |
Transaccion SLG1
Desde esta transacción podemos ver todos los logs guardados en el sistema:




Comentarios
Publicar un comentario